Government Employees Pension System
History
The Government Employees Pension Act, Korea's first public pension system, was enacted in 1960, and the Military Pension Act, Private School Pension Act and the National Pension Act were implemented in 1963, 1972 and 1988, respectively. Commencing with the first reformation of the Government Employees Pension Act in 1995, a total of 4 pension reforms have since been achieved.
Overview
The Government Employees Pension System is a legislation which guarantees social protection for government employees and their surviving spouses by providing comprehensive benefits such as retirement pensions, survivors and disability pensions or other lump-sum payments.
Eligibility
- A government employee under the State Public Officials Act, the Local Public Officials Act or other Acts
- Other persons prescribed by Presidential Decree among the employees working in government agencies or local governments
* Persons excluded : Military personnel and public officials inaugurated by election.
Financial Management
Government employees’ pension benefits are disbursed from the funds that consist of the employee contributions paid by government employees, employer contributions borne by the state and local governments, and any profits taken from the fund management.
If such a case arises where the yearly income cannot cover the expenses for the year, then the shortage shall be covered additionally by the state and local governments to ensure the stable disbursement of the planned benefits.
Moreover, in order to fulfill its role as the government employees’ pension fund, since 2015, part of the profits from the fund investment have been diverted into the pension fund.
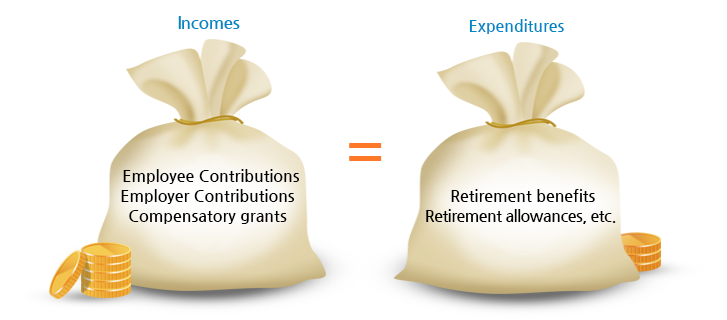
- Profits
- 1) Employee Contribution (government employees)
- 2) Employer Contributions (State, local government)
- 3) Compensatory grants, etc.
- Expenditures
- 1) Retirement benefits (pension, lump-sum)
- 2) Retirement allowances, etc.
Various benefits under the Government Employees Pension Act are funded by the "employee contributions" deducted at a fixed ratio of the standard monthly incomes of government employees and the "employer contributions" borne by the state or local government at a fixed ratio of the remuneration budget.
- Current percentage of "Employee Contributions" and "Employer Contributions"
| Employee Contributions | Employer Contributions |
|---|---|
| 9% of the standard monthly income | 9% of the remuneration budget |
Types of Benefits
| Classification | Types of Benefits |
|---|---|
| Retirement benefits | Retirement pension (or early retirement pension) |
| Lump-sum retirement pension after deduction | |
| Lump-sum retirement pension | |
| Lump-sum payment on retirement | |
| Survivors' benefits | Survivors' pension |
| Lump-sum survivors' pension | |
| Lump-sum payment to survivors | |
| Additional payments to survivors' pension Special additional payments to survivors' pension | |
| Retirement allowance | Retirement allowance |
